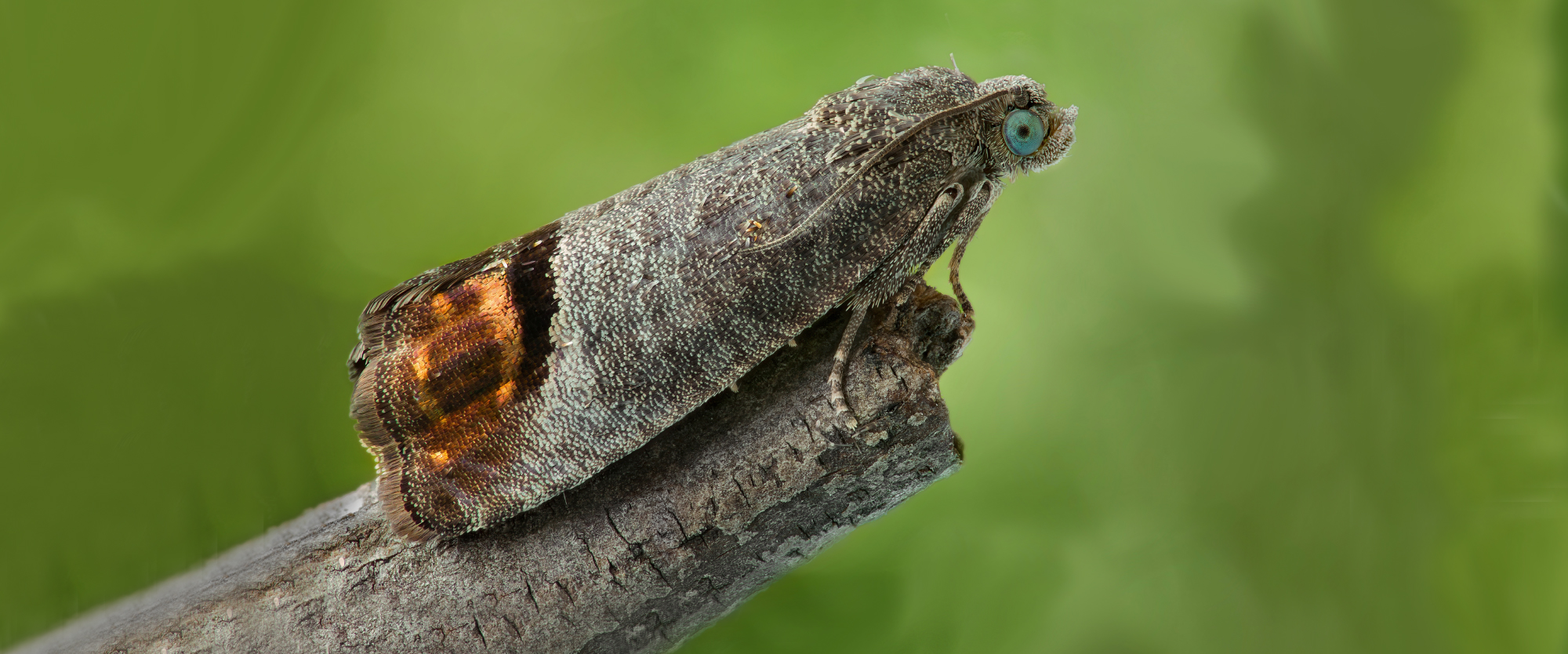
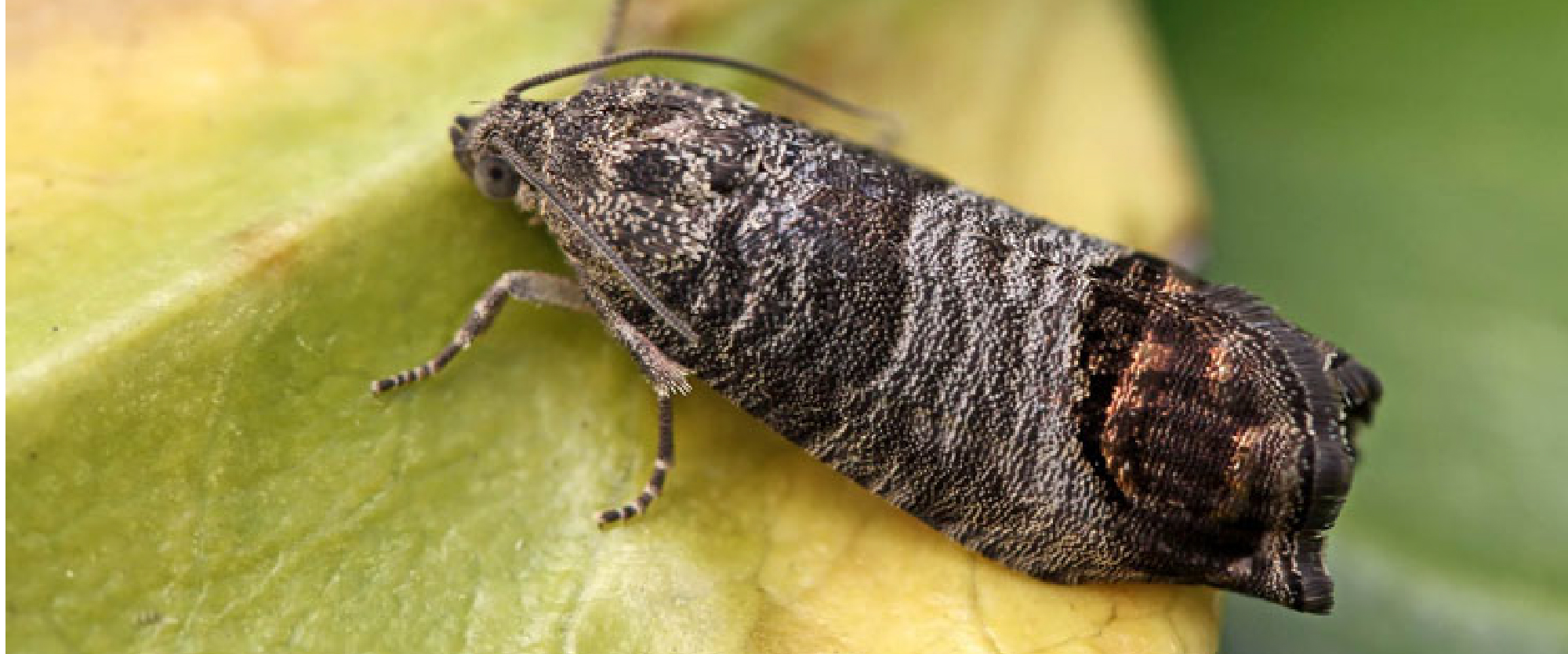
The codling moth (Cydia pomonella) is a member of the Lepidopteran family Tortricidae. Not large, they are distinguished from other moths by the golden patterns on their fore-wings: brown spots enclosed in gold, coppery bands. The codling moth young larvae are white with black heads while mature larvae are pinkish white with brown heads. The preferred host plants are apple and pear trees.
Damage
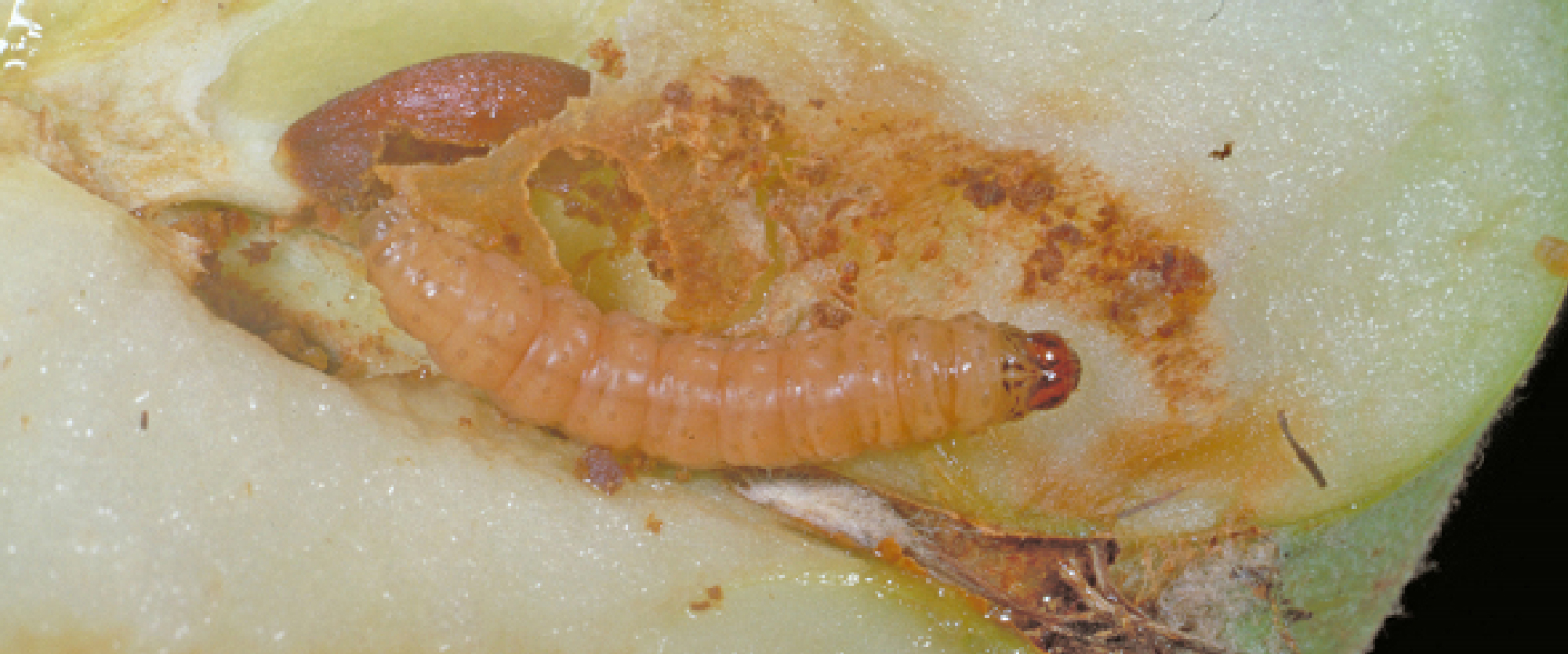
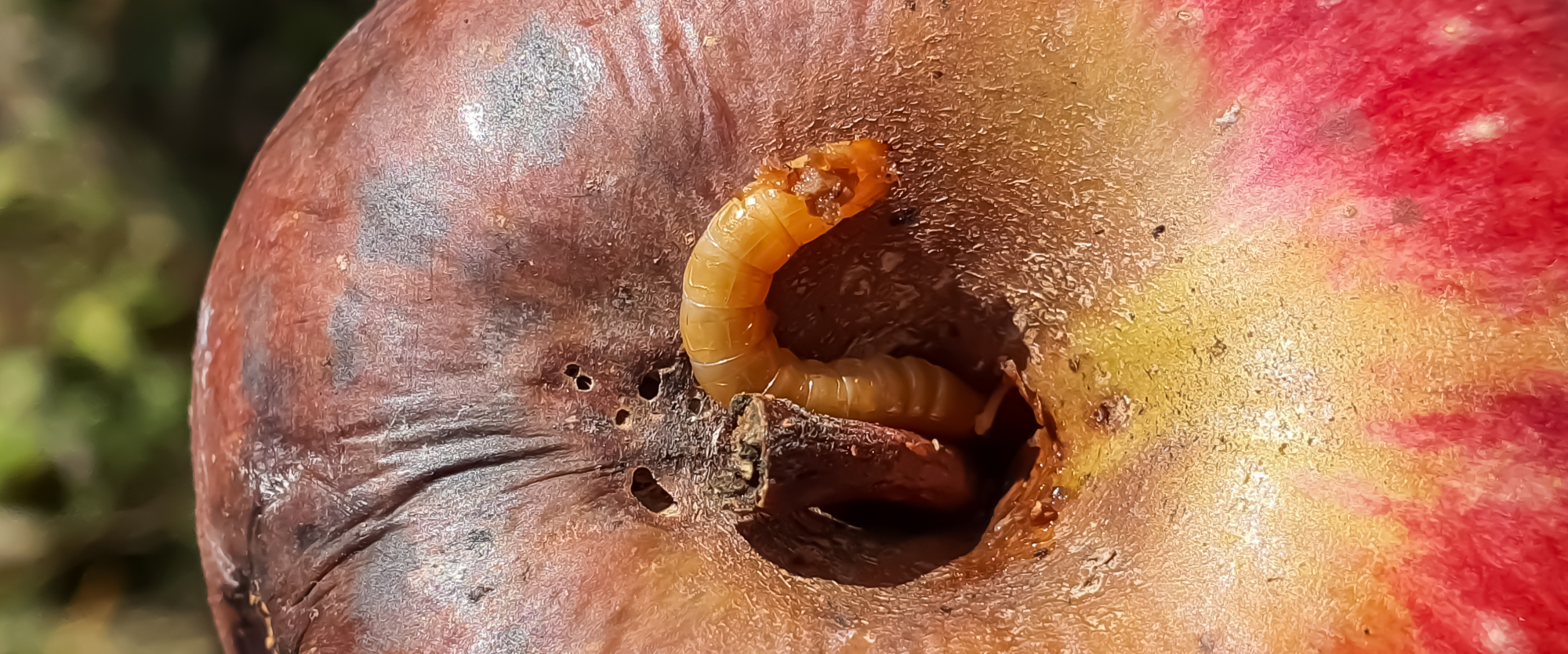
When larvae feed minimally on the outside of the fruit, they create small “stings” on the surface of the fruit, When the larvae penetrate the fruit and tunnel to the core, feeding on the pulp and seeds they cause extensive interior breakdown of the fruit tissue leading to premature fruit drop. the exit hole (where mature larvae emerged) is often covered with frass. A reddish-brown discoloration can be observed at the point of penetration as well as an increase in the incidence of mold and disease. The point of entry becomes an open door to other pests and pathogens.
There are specific natural enemies and sustainable solutions for different species of moths.
For more information contact your local BioBee field agent.